Озон (O₃) — мощный окислитель, образующийся при воздействии электрического разряда (коронный разряд) или ультрафиолетового излучения на молекулярный кислород (O₂). Обладая высокой реакционной способностью и коротким периодом полураспада, озон быстро распадается на молекулярный кислород без образования устойчивых токсичных остатков, что делает его привлекательным агентом для экологически безопасной дезинфекции [1].
Озон оказывает комплексное действие: бактерицидное, вирулицидное, окислительное и дезодорирующее. В отличие от традиционных химических дезинфектантов, таких как хлор, озон не образует значительных количеств токсичных побочных продуктов, например тригалометанов, и не оставляет запаха после обработки [2]. Скорость инактивации микроорганизмов озоном в 3000–10 000 раз превышает таковую у хлора при одинаковых условиях [3]. Вследствие этого озонирование широко применяется в очистке питьевой и сточной воды, обработке воздуха, дезинфекции поверхностей, а также в пищевой промышленности и медицине.
Механизм антимикробного действия озона
Озон воздействует на микроорганизмы преимущественно через прямое окисление ключевых структурных компонентов клеточной оболочки и внутриклеточных макромолекул. У грамотрицательных бактерий, таких как Escherichia coli, озон разрушает наружную мембрану за счёт окисления фосфолипидов и липопротеинов, что приводит к нарушению целостности клеточной стенки и образованию микропробоин [4]. Дальнейшее проникновение озона в цитоплазму вызывает окислительный стресс, сопровождающийся повреждением белков, липидов и нуклеиновых кислот. В частности, экспериментально подтверждено повреждение кольцевой плазмидной ДНК, что нарушает репликацию и приводит к летальному исходу [5].
Схематически механизм действия можно представить следующим образом (рис. 1):
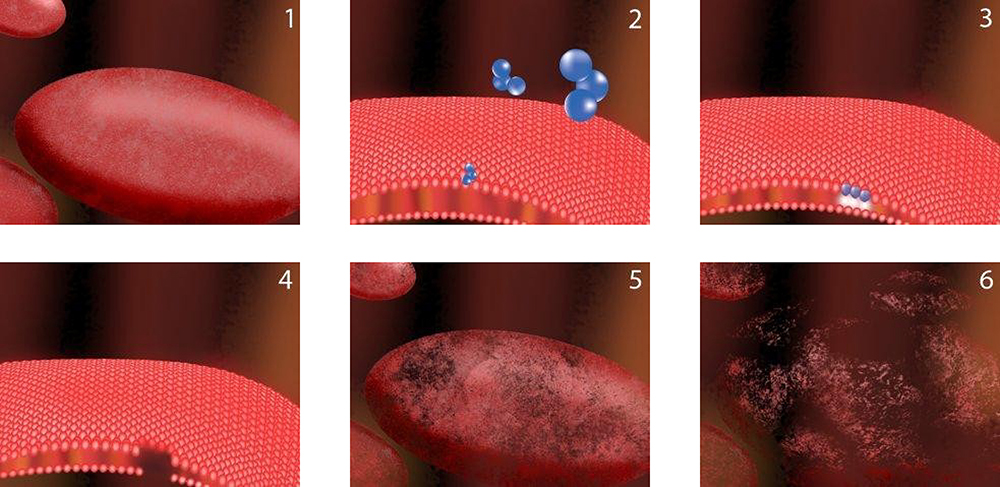
Рис. 1. Схема действия озона на грамотрицательную бактерию
- Здоровая бактериальная клетка с сохранными клеточной стенкой и цитоплазматической мембраной.
- Молекула озона (O₃) взаимодействует с наружной мембраной.
- Окисление фосфолипидов приводит к образованию пероксидов и разрыву мембраны.
- Формирование «пробоин» в клеточной стенке.
- Деформация клетки и утечка цитоплазмы.
- Полное разрушение структурной целостности — клетка погибает.
Особую устойчивость к озону проявляют споровые формы бактерий (например, Bacillus и Clostridium spp.), а также микобактерии, обладающие сложной липидной оболочкой [6]. Тем не менее, при достаточной концентрации и времени контакта (так называемый CT-фактор, мг·мин/л) озон эффективен даже против этих резистентных форм.
Эффективность озонирования в отношении бактерий
В таблице 1 представлены данные по инактивации различных бактерий под действием озона в водной среде. Как видно, чувствительность микроорганизмов варьируется в зависимости от таксона, формы (вегетативная/споровая) и матрицы (чистая/загрязнённая вода).
Таблица 1. Эффективность озонирования в отношении бактерий
|
Микроорганизм
|
Условия
воздействия
|
Эффект
|
Источник
|
|
Bacillus
sp.
|
c = 0,2 мг/л,
30 с
|
Полное
разрушение клеток
|
[7]
|
|
Bacillus
cereus (вегетативные)
|
c = 0,12
мг/л,
5 мин
|
99 %
инактивации (в воде)
|
[8]
|
|
Bacillus
cereus (споры)
|
c = 2,3 мг/л,
5 мин
|
99 %
инактивации (в воде)
|
[8]
|
|
Escherichia
coli (чистая вода)
|
c = 0,25
мг/л,
1,6 мин
|
99,9 %
инактивации
|
[9]
|
|
Escherichia
coli (загрязнённая вода)
|
c = 2,2 мг/л,
19 мин
|
99,9 %
инактивации
|
[9]
|
|
Mycobacterium
avium
|
c = 0,17
мг/л,
2 мин
|
99,9 %
инактивации (в воде)
|
[10]
|
|
Pseudomonas
aeruginosa, Salmonella enterica
|
—
|
Высокая
чувствительность
|
[3, 11]
|
|
Vibrio
cholerae
|
—
|
Сверхчувствительность
|
[12]
|
Примечание: наблюдается эффект «всё или ничего» — ниже пороговой концентрации озона эффект отсутствует, выше — происходит полная инактивация. Пороговое значение концентрации зависит от типа микроорганизма и матрицы [13].
Действие озона на вирусы
Вирусы, в отличие от клеточных организмов, не обладают ферментативными системами детоксикации и защиты от окислительного стресса. Вирусы с липидной оболочкой (например, Influenzavirus, Herpesviridae) особенно чувствительны к озону из-за лёгкого окисления липидов мембраны. «Голые» вирусы (без липидной оболочки), такие как Poliovirus и Hepatitis A virus, более устойчивы, но также подвержены инактивации при достаточных CT-параметрах [14].
Таблица 2. Эффективность озонирования в отношении вирусов
|
Вирус
|
Условия
воздействия
|
Эффект
|
Источник
|
|
Bacteriophage
f2
|
c = 0,41
мг/л,
10 с
|
99,99 %
инактивации
|
[15]
|
|
Coxsackievirus
A9
|
c = 0,035
мг/л,
10 с
|
95 %
инактивации
|
[16]
|
|
Coxsackievirus
B5
|
c = 0,4 мг/л,
2,5 мин
|
99,99 %
инактивации
(в сточных водах)
|
[17]
|
|
Hepatitis
A virus
|
c = 0,4–0,6
мг/л, 1–2 мин
|
99,5 %
инактивации
|
[18]
|
|
Poliovirus
|
c = 0,3–0,4
мг/л, 3–4 мин
|
99,99 %
инактивации
|
[19]
|
|
Vesicular
stomatitis virus (VSV)
|
c = 0,1–0,2
мг/л, <30 с
|
Полное
разрушение
|
[20]
|
Пороговые концентрации варьируются от 0,035 мг/л (Coxsackievirus A9) до 0,6 мг/л (Hepatitis A virus), что подчёркивает необходимость индивидуального подхода к дозированию в зависимости от задачи.
Обсуждение
Полученные данные подтверждают высокую эффективность озонирования как метода дезинфекции. Однако его практическое применение ограничено рядом факторов. Во-первых, эффективность озонирования строго зависит от CT-фактора (произведение концентрации озона на время контакта), который должен быть адаптирован под тип микроорганизма, матрицу и условия среды (pH, температура, содержание органики) [3]. Например, E. coli в загрязнённой воде требует в 10 раз большей дозы и в 10 раз более длительного времени воздействия по сравнению с чистой водой из-за конкуренции за озон со стороны органических веществ [9].
Во-вторых, в проточных реакторах, где время контакта ограничено, достижение достаточного CT-фактора затруднено. Это приводит к неполному обеззараживанию, особенно в присутствии органических загрязнений, которые расходуют озон на побочные реакции [2]. В таких условиях озонирование может оказаться недостаточным для надёжной инактивации устойчивых патогенов, таких как Cryptosporidium или Adenovirus.
Кроме того, риск образования побочных продуктов окисления (альдегидов, кетонов, карбоновых кислот) требует последующей доочистки, например, с помощью активированного угля или биологических фильтров [1].
Заключение
Озонирование представляет собой высокоэффективную и экологически безопасную технологию дезинфекции, способную инактивировать широкий спектр патогенных микроорганизмов, включая устойчивые к традиционным методам штаммы. Однако его эффективность строго зависит от концентрации озона, времени контакта и характеристик среды.
В проточных системах, где время контакта ограничено, эффективность озонирования существенно снижается.
Следовательно, для применения в реальных условиях, особенно в системах воздухоочистки с высоким потоком, озонирование целесообразно комбинировать с другими методами.
Список литературы
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, 4th ed. Geneva: WHO, 2017
- US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Alternative Disinfectants and Oxidants Guidance Manual, 1999
- Rice, R.G. Ozone in Water Treatment: Application and Engineering. 2003
- Kim, J.Y. et al. Mechanism of bacterial disinfection by ozone // Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 1999. Vol. 65, no. 1
- Shin, G.A. et al. Inactivation of surface-associated enteric viruses on strawberries by gaseous ozone and ozone-based sanitizers // Journal of Food Protection. 2000. Vol. 63, no. 12
- Matsumoto, N. et al. Inactivation of microorganisms by gaseous ozone // Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy. 2004. Vol. 10, no. 5
- Chang, E.E. et al. Effects of ozone on the inactivation of Bacillus subtilis // Ozone: Science & Engineering. 1985. Vol. 7, no. 2.
- Kim, M.B. et al. Ozone inactivation of Bacillus cereus spores in water // International Journal of Food Microbiology. 2003. Vol. 85, no. 1–2.
- Chang, N.-B. et al. Ozone disinfection of E. coli in water: effect of turbidity and organic matter // Water Research. 1998. Vol. 32, no. 12
- LeChevallier, M.W. et al. Inactivation of Mycobacterium avium by chlorine, chlorine dioxide, and monochloramine // Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 1996. Vol. 62, no. 10
- Ballester, N. et al. Ozone disinfection of Salmonella and Pseudomonas in water // Journal of Applied Microbiology. 2008. Vol. 105, no. 4
- Sobsey, M.D. et al. Inactivation of health-related viruses by chemical disinfectants // Progress in Industrial Microbiology. 1989. Vol. 27
- Finch, G.R. et al. Ozone inactivation of Cryptosporidium: a review // Ozone: Science & Engineering. 1993. Vol. 15, no. 3
- Thurston-Enriquez, J.A. et al. Inactivation of human enteric viruses by ozone // Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2003. Vol. 69, no. 2
- Roy, D. et al. Mechanistic implications of viral inactivation by ozone // Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 1981. Vol. 41, no. 3.
- Vaughn, J.M. et al. Inactivation of selected enteroviruses in wastewater by ozone // Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 1979. Vol. 37, no. 1
- Chang, J.C. et al. Ozone inactivation of Coxsackievirus B5 in secondary effluent // Water Research. 1985. Vol. 19, no. 5
- Payment, P. et al. Inactivation of hepatitis A virus and Rotavirus in water by ozone // Canadian Journal of Microbiology. 1988. Vol. 34, no. 10
- Bell, C.R. et al. Ozone inactivation of poliovirus in water // Canadian Journal of Microbiology. 1973. Vol. 19, no. 6
- Rusin, P. et al. Comparative surface-to-surface transmission of Vesicular stomatitis virus and SARS-CoV-2 under simulated environmental conditions // Journal of Applied Microbiology. Vol. 93, no. 3
